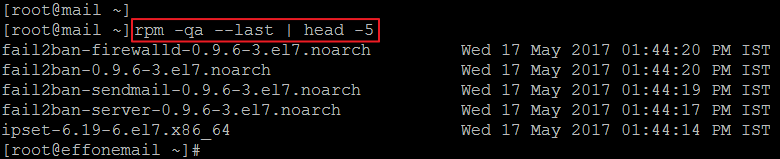
One of the several duties of a system administrator is to in this case and in order keep on your system, you can learn, and/or keep in mind a few quick commands.In this article, we will explain how to list all installed rpm packages on CentOS, RHEL and Fedora distributions using four different ways. Using RPM Package Managerformerly known as Red-Hat Package Manager is an open source, low-level package manager, which runs on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) as well as other Linux such as CentOS, Fedora and UNIX systems.You can compare it to, the default packaging system for Debian and it’s derivatives such as Ubuntu, Kali Linux etc.The following command will print a list of all installed packages on your Linux system, the flag -q meaning query and -a enables: # rpm -qa.
Since the release of Fedora 22, in which DNF became the new default packaging tool and therefore obsoleted on subsequent Fedora OSs, YUM was kept on those Fedora OSs for compatibility reason regarding Linux distributions forked from the Fedora project (Red Hat, Centos) that kept on using YUM, and will be kept for that very reason until they adopt it definitively.I had little time before your previous post as reply, to test a command of my investigation that also relies as well on expression ‘ wc -l‘. Such command is likely to cover all current active repositories on a system which is indeed exactly what I was aiming to.Here are for comparative purpose the following commands (by the way, there is no need to be executed as user root): ‘ dnf list installed wc -l‘, ‘ rpm -qa wc -l‘ respective outputs: 1619, 1590.As noticeable those outputs are incorrect which is no surprise after investigation. Their subsequent commands are inappropriate; they do not reflect exclusively the current active repositories on my system, which in that case are fedora, updates which respectively contain 54 801, 13 085 packages (subsequent results are available from another command too).
How To Install Packages In Rhel 7 3
Good luck though in your hobby.

Hi,Even after creating the link, the python version is still showing the same:root@XXX pip# which python2.7/bin/python2.7root@XXX pip# ls -l /bin/pythonlrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Apr 13 2017 /bin/python - python2root@XXX pip# ls -l /bin/python2lrwxrwxrwx.
Redhat Packages
1 root root 9 Apr 13 2017 /bin/python2 - python2.7root@XXX pip# ls -l /bin/python2.7-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 7144 Aug 2 2016 /bin/python2.7root@XXX pip# echo $PATH/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/binroot@XXX pip# ln -s /usr/bin/python3.6 /usr/local/sbin/python^Croot@XXX pip# ln -s /bin/pythonpython python2 python2.7 python3 python3.4 python3.4mroot@XXX pip# ln -s /bin/python3.4python3.4 python3.4mroot@XXX pip# ln -s /bin/python3.4 /usr/local/sbin/pythonroot@XXX pip# python -VPython 2.7.5root@XXX pip# which python/usr/local/sbin/pythonroot@XXX pip#.